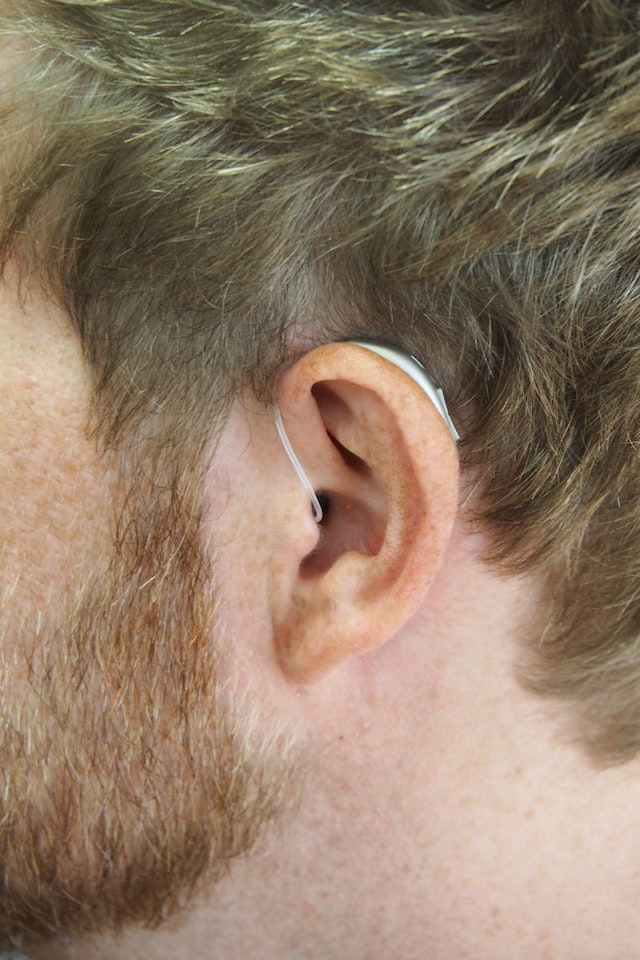
Whether you’re new to hearing devices or you’re simply interested in learning more about them, there are several things you should know about how they work. You should first know that they use bone conduction, digital or in-the-canal technology, to send sound to your ear.
In-the-ear
Those who have hearing loss can benefit from Phonak’s hearing aid solutions like using in-the-ear hearing devices. These are custom-molded to fit inside the ear. These devices are available in various styles and are designed to help people with mild to severe hearing loss. These devices are also easy to use, making them a good choice for people with hearing difficulties. These devices are designed to be discreet and are usually small in size. Some even fit behind the ear, making them perfect for those with reduced dexterity. These in-the-ear devices are comfortable and easy to adjust. They can be either an entire shell or a half shell. The shell is made of titanium, which makes it one of the most rigid materials on the market. The faceplates can be made in various colors to blend with your skin tone. Depending on the style of the device, you can adjust the amount of sound that the speaker produces. A battery powers the hearing aids. The batteries need to be changed every three to 20 days. In addition, wind can impact sound quality. The in-ear hearing aids are more comfortable than the larger devices. Some in-the-ear hearing devices are equipped with Bluetooth technology. This can make it easier to connect your device to various electronics. These devices are also more durable than other hearing aids, which can last longer.
In-the-canal
In-the-canal hearing aids can be customized to fit the anatomy of the ear. Typically, in-the-canal hearing devices are designed for placement substantially inside the ear canal. They are usually larger than invisible hearing aids and can be more comfortable to wear. They are also less noticeable and offer lower feedback from noises, such as telephone sounds. In-the-canal hearing devices can be made for both the bony and cartilaginous regions of the ear canal. Having a device that is shaped to match the anatomy of the ear is essential. The ear canal is generally oval, with a long diameter on the vertical axis and a short diameter on the horizontal axis. The bony region’s diameter can be as small as 3.8 mm. The acoustic seal was made from a soft compliant material, such as a rubber-like polyurethane. It was designed to compress against the walls of the ear canal, sealing the ear canal from the outside. It was about 1.5 mm thick and consumed about 3 mm of ear canal before compression.
The battery module is a disposable removable component that delivers power to the main module. The unitary structure of the disposable battery module makes it easier to handle and manipulate. It includes a sound port, a battery, a microphone, an electromechanical connector, and an acoustically transparent debris filter. It can be placed over or under the sound port. The acoustically transparent debris filter helps to prevent water from reaching the microphone.
Bone conduction
Surgically implanted bone conduction devices convert acoustic sound waves into mechanical vibrations and transmit these signals to the inner ear. These devices have an external part held in place magnetically or an internal interest that generates mechanical forces against the skull. They are available in two types: passive and active. In the early years, bone conduction devices were placed on the head with a band or eyeglasses. After the bone healed, the device would snap into the abutment.
Bone conduction hearing aids are designed to be used by patients with conductive hearing loss. This type of hearing loss is caused by damage to the outer and middle ear and chronic ear infections. In addition to restoring hearing, bone conduction devices also reduce the risk of infection in the ear canal. Because these devices don’t rely on the eardrums for sound, they are more comfortable than standard hearing aids. If you’re interested in bone conduction hearing devices, your otolaryngologist can help you decide which one best suits your needs. Your health plan will also impact the cost of an implant. Bone-anchored hearing aids are ineffective for those with severe ear malformations and don’t work for single-sided deafness. However, these devices can be beneficial for children with mixed hearing loss. This is because they can bypass particular problems and send sound directly to the inner ear.
Cochlear implants
Several government programs offer to fund cochlear implants and hearing devices for the deaf. This has been a long-standing practice, and successive governments have maintained the funding arrangement. Many private health insurers do not cover the cost of a cochlear implant, although the company’s speech processors are covered under general treatment policies. There are two main types of cochlear implants. These include acoustic and bone-anchored devices. The acoustic instruments are used to help people hear better, while the bone-anchored devices are used to improve the strength and stability of a person’s hearing. The acoustic device is a small cochlear implant that can be fitted into the ear and is designed to deliver an audible sound. Its size varies. It is an excellent example of the technological advances made to make hearing possible. One of the most critical advances in cochlear implants is the ability to implant a cochlear device in the ear of a person who is deaf. The device is acoustic in design, but it is also a sophisticated technology designed to give a person’s brain the necessary information to interpret it. Several factors play a part in this technology. Among these are the type of sound the device produces and how the acoustic instrument is shaped. The shape of the acoustic device is crucial because the more the sound acoustic device resembles the ear, the more successful it will be in helping people hear.